The Role and Priorities of International Development Agencies to Democratic Governments’ towards Education and Research in Africa: Educationists Perspective-Juniper Publishers
Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Social Sciences & Management studies
Introduction
The ultimate objective is to examine the roles and
priorities of the International Development Agencies or organisations in
education and research to African countries. And the research question
is how good, or important such supports given to African governments,
projects the growth of African continent? The essence of this study is
to review the challenges faced by Africa Democratic Governments in a
short change of staggering education and research delivery policies and
systems, hence, confounding the development of specific educational and
research policies. This is to establish scholarship challenges at the
advance stage of nation building where access to scholarship or
government sponsorship at national level is poorly managed by delivery.
Human Resource Management Troubles in Education Sector
Teaching staff absenteeism is due to low pay, the
brain drains of qualified teachers from the teaching profession and
informal user fees being charged, according to UNICEF. UNICEF has
reported that real pay levels of public sector employees are
falling, and it is further, reviewed at the recent IMF report which,
shows that most African countries were being advised by the IMF to cut
public sector wage bills in 2009 to 2011 [1].
Academic Research Citation Indexing within African Context
It is further stated that Sub-Saharan Africa has been
very successful in research output and citation impact. Regions such as
Southern and East Africa has improved their average quality of research
output because it is now above the world average (i.e. normalized to
1). But about the West and Central Africa have nearly doubled their
share of articles published globally and even though, their citation
impact has not increased and remained relatively constant. More to this,
is that, Africa’s research capacity improvements have been closely tied
to the high levels of international collaborations, that is, between
African based researchers and those in Western countries [2,3]. It has
revealed that over 70% of all research publications from Southern and
East Africa have been co-authored with an international collaborator
[4]. Also, they stated that “collaboration and working with Western
researchers is one way for Africa to improve its research
capacity and sending researchers abroad or welcoming outside
researchers to Africa is another highly effective enabling tactic.”
The report found out that ‘transitory researchers’, that is, “those
that spend less than two years in Africa or abroad, are far more
productive and on average produce research of a higher impact
research than researchers who have not had the opportunity to
perform research outside of the continent” [4].
It is however recommended that while African authors have
nearly doubled by sharing their articles over the past decade,
it is hoped that the returns could be many times greater over
the next decade if awareness of usage and research capacity
are done in a collaborative and integrated manner by African
institutions via access programs and publishers. Elsevier,
since 2001, has been deeply engaged in programs to foster the
growth of the African science community and support to African
researchers to develop and enhance their research output and
quality. Elsevier is a founding publisher of Research4Life, which
is a public private partnership in tackling access of research in
developing countries. Elsevier supplies over a quarter of “44,000
books, journals and databases available to doctors, researchers
and policymakers in Africa, and across more than 100 developing
countries.” With the Elsevier Foundation’s Innovative Libraries
in Developing Countries Program, they provided annual grants
totalling $300,000 donated to projects that build infrastructure,
improve information literacy, repositories, and provide training
to boost overall usage of Research4Life resources in Africa and
beyond [4].
The Government Function as an Organisation in Nation DevelopmentNew Public Administration Policy Systems and Management
The public services must always respond to important
requirements and the needs concerning the higher level of
citizens’ satisfaction of a nation [5]. All what these existing and
previous literature talks about is New Public Administration
(NPA) and New Public Management (NPM) and with these, it
deliberates on the issues relating to World Bank, IMF, EU and
so on, their overall global policy implementations on the third
world countries – Africa. The existing literature researched,
concentrated more on developmental agencies and Donor
partners work for African countries and has few discussions on
the history of Public Administration in the developed world. New
Public Management (NPM) reforms in the advanced countries
happens in the era of Structural Adjustment Programmes (SAP),
a process which was driven by a combination of economic,
social, political and technological factors of service delivery in
responds only to satisfy external players like the World Bank,
IMF, EU, USA, OECD etc and not from the total will of people per
se (Doe 2005). According to (Doe 2005), he stated that Ghana
has not been matured through any recognisable technocratic,
systematic, or policy-making approach in the past decades or
since independence, except that it had, but just a mimicked kind
of public service administration and management practices
through coercion/force/pressure from the developed countries
and the International Development Agencies.
Public Sector Administration to Boost Organisational Development
Even, civil servants are developed into a lethargic and
passive body whereby their functions are disconnected from the
citizens and have no interest in adopting an active role in the
service of the state [6]. Governance is a broad term that includes
values and practices such as legality, justice, trust in laws and
institutions, efficiency, responsible budgeting, management of
human resources and crisis management [6]. Notwithstanding,
the same existing literature talks about the challenges involve
in the delivery of good governance in the public sector of
economies. And the problem is, has the citizens have say in the
governance process, or when it comes to establishing policies
and programmes, how often have they been consulted and in
what manner and channel? Are the people happy with the way
government establishes and delivers its programmes?
Problem with Internal Generated Funds in Africa to Support Government Policies
According to Annan [7], noted the need for curbing the
menace of corruption and weak governance together with
international tax avoidance and evasion, which are the main
crucial matters that affect democratic governments in Africa,
and this makes it impossible for people of Africa to benefit from
their continent vast natural mineral resources and wealth. At
the forum, it was stated that the African continent is losing more
through illicit or unsolicited financial outflows than it receives
in aid and foreign direct investments as the general view is
perceived by World of Business indicators and reports [8]. What
the forum found in their report was that trade mispricing or
losses are associated with the misrepresentation of export and
import price values by African dealers, together with other illicit
outflows which cost the continent $38.4-billion and $25-billion
respectively between 2008 and 2010. Mr. Kofi Annan advocated
for the G20 a rule-based global system on tax transparency to be
developed. “All foreign-owned companies should be required to
disclose the ultimate beneficiaries of their profits,” [7].
The IMF
The IMF
This situation continues due to the ideologies entrenched
in the field of economics and are taught in schools about
monetarism. Even countries without under the IMF strict loan
programs, they are still faced with IMF restrictions, if not,
there should be investment in higher public sectors of work
but due to the IMF biases in ideological sense that underpin
their conventional monetary policies makes it difficult for such
countries to flourish. It is obvious that many current finance
ministries and central banks officials who have gone to school
in the last 26‐36 years have largely been taught one thing, and
one thing only, which is that the only “prudent” and “sound” option for fiscal and monetary policies is the very conservative
one favoured by the Reagan and Thatcher governments, which
were suddenly introduced in the school of monetarism within
neoclassical economics. Because of this assertion, all other viable
options which is actual and that would allow for higher public
investment have subsequently been dismissed as “imprudent”
and “unsound”. Therefore, the problem is much more bigger than
just the IMF because even if a country does not currently have an
IMF loan program, but it means its fiscal and monetary policies
are still likely to be subjected to the same sharp right‐wing turn
that has been taken into the economics profession for over 36
years ago, from which it’s yet to recover or find solutions to Kyrili
and Martin [9] (Figure 1).
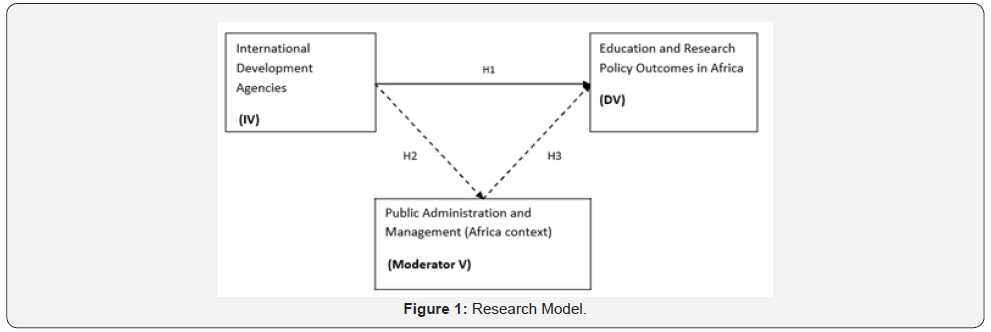
Research Methods
This is an empirical study and therefore, its sampling
technique has been non-probability sampling, hence, a
convenience technique was adopted through as a questionnaire
administered through social media WhatsApp platforms
and emails. Out of this process 5 participants responses are
been used for this data analysis and discussion and of which
conclusion is drawn. Educationists were the target participants
for this research and therefore a convenience sample response
of 54 participants has been sorted. The questionnaire was
designed using Google Forms as online survey tool. Therefore,
a future probability study is required to ascertain the efficiency
and significance of this topic as another way of supporting
these current data findings. This includes reliability testing
with SmartPLS, and the use of Fuzzy Delphi Method - shows
mathematically uncertain phenomena within the environment
[10]. Excel spreadsheet was used for the pie chart of respondents
(Figure 2).
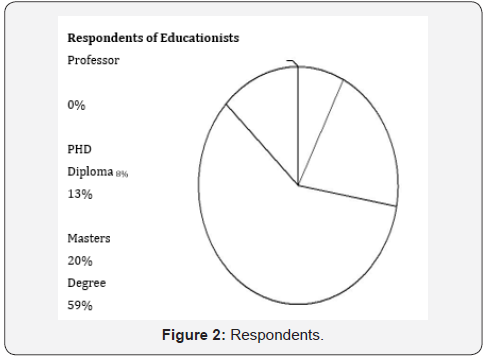

From Table 1 and chart represents the target respondents
of this research totalling 54 responses. Out of this number,
59% were degree holders, 20% were Masters’ holders, 13%
were Diploma holders, and 8% were PhD holders. Whereas no
Professor gets to respond to the questionnaire due to may be the
use of the social media systems and platforms such as whatsApp
of link and emails of the links been sent. But this also signifies
that the target of this research has been achieved because all
those participated can be classified as educationists (Figure 3).
PLS Algorithm
With the construct above shows the values of the
factor
loadings to each variable and the corresponding effects of the
moderator variable and the dependant variable on the IDA
as independent variable. In the blue indicates the R Squares
whereas the arrows show the relationship effects that takes place
between the variables with regression rates (can be positive or
negative). And so, by convention, path loadings should be above
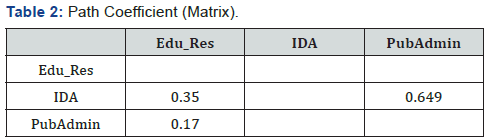
0.70 [11,12]. For this research, none has dropped (Table 2). The
path from IDA to Edu_Res is positive coefficient of 0.350 and IDA
to PubAdmin is positive coefficient of 0.649 whereas, PubAdmin
to Edu_Res is positive coefficient of 0.170. These means that IDA
to PubAmin as a moderator variable has stronger relationship
than, as a moderator in executing or having a less final impact
and effect towards Edu_Res. Path coefficients are standardized
with weights which varies between -1 to +1. Therefore, weights
closet to 1 is the strongest coefficient path and weights close to 0
are the weakest coefficient path (Table 3).


The above means that about 23% of the variance in Edu_Res
is explained in the model (i.e. between IDA and Edu_Res). Also,
about 42% of the variance in PubAdmin is explained in the
model from IDA to PubAdmin as a moderator variable towards
the independent variable Edu_Res at 23% model explained all
together. Hence, there is an indirect effect within this model
as IDA to PubAdmin to Edu_Res. Chin [13], Höck & Ringle [14]
describes results above the cut-offs 0.67, 0.33 and 0.19 to be
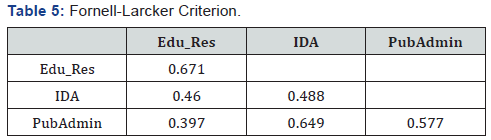
“substantial”, “moderate” and “weak” respectively (Tables 4-6)
(Figure 4).
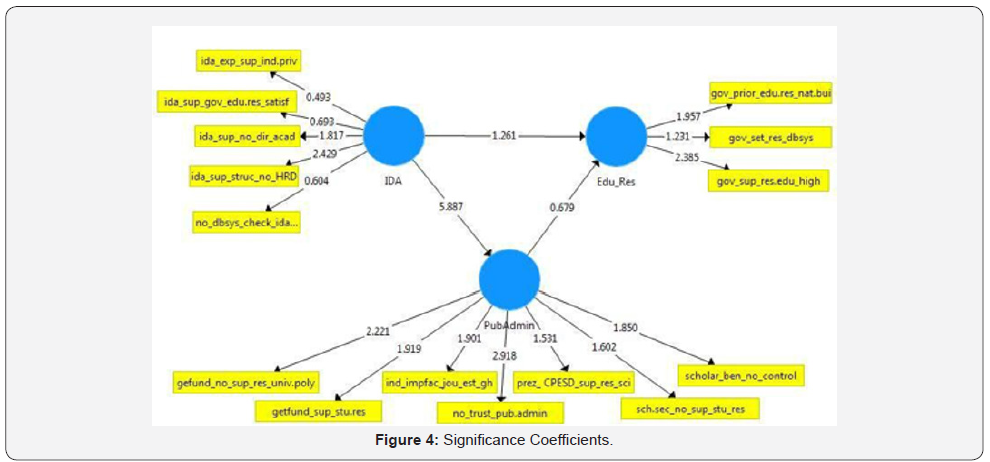
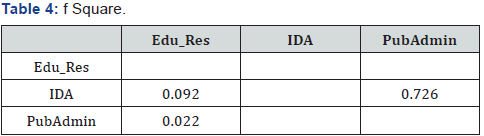
Composite Reliability
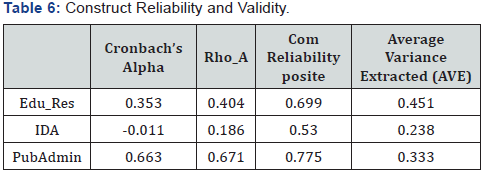
From Table 7 shows that there is reliability at Edu_Res and
PubAdmin as an adequate model whereas IDA is very weak
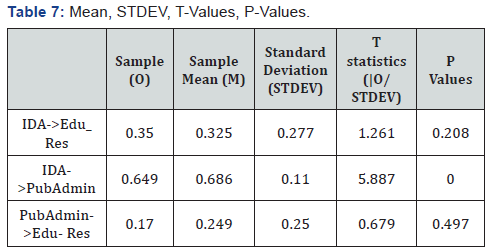
composite (Table 7). It is noted that, all t-values above 1.96 are
significant at 0.05 levels [12]. Therefore, according to the t values
in the above table show that IDA to Edu_Res is not significant as
well as PubAdmin to Edu_Res is also not significant. But the t
value of IDA to PubAdmin is very significant at 5.887. More so,
according to the p-value at p>0.05 means that IDA to Edu_Res
is insignificant at p=0.208 because it supports the fact that
IDA support for Edu_Res is not IDA major policy. Also, IDA to
PubAdmin (government) is significant in the sense that p=0.000,
hence, it confirms that IDA only has a policy of given support to
the PubAdmin (government) and not probably support any other
development or project. Finally, PubAdmin (government) to Edu_
Res is weak evidence since p<0.5 which means that PubAdmin in
turn does not really use the support received by IDA’s to build
or support Edu_Res (Table 8). The above shows that CI at 97.5%
level of IDA to Edu_Res is between, -44% to 70%. Also, the CI
of 97.5% level of IDA to PubAdmin (government) is within 43%
and 86%, whereas the CI of 97.5% level of PubAdmin to Edu_Res
is between -24% to 80%. This simply means that the confidence
level of this data is IDA to PubAdmin (Table 9).
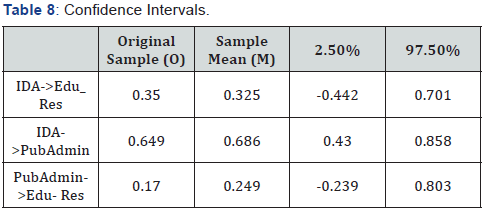

To determine certainties, CI bias is corrected as above as IDA
to Edu_Res as a bias of almost -2% with a corresponding 97.5%
confidence level corrected between, -63% to 68%. Moreover, the
bias of IDA to PubAdmin is positive 4% with a corresponding
97.5% confidence level corrected from 20% to 79%. Meanwhile,
PubAdmin to Edu_Res bias is 8% with a corresponding 97.5%
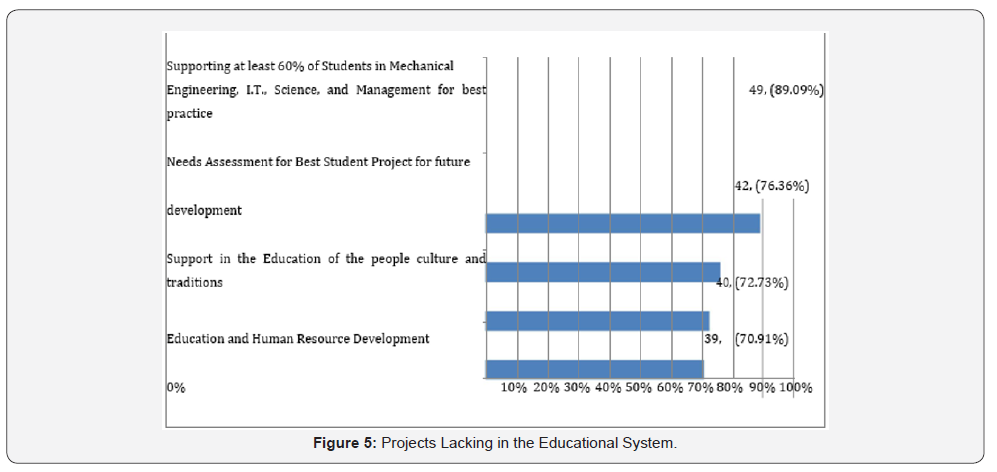
confidence level corrected as -51% to 57% (Figure 5). From
the above clearly shows that all the projects listed are lacking
in the educational systems and operations of research in the
educational curricular. Policies to support such projects are
minimal in nature and hence, lack the implementation of such
projects across board.
Conclusion and Recommendation
According to Power [15] we noted that fears has been
expressed over the education and research in the 21st century
were countries in the global world would be more competitive
and therefore, education must be a human right rather than
been traded as a marketing commodity, where high prices
would made impossible for the intelligent poor to benefit. Power
said, “If we fail, I fear that our world will become increasingly
unequal, competitive, polarised, conflicted and dangerous” [15].
Power [15], UNDP [16], report warned that anytime market
prices goes too far and become dominance towards social and
political motives, the outcomes, the opportunities and rewards of globalization expand unequally and inequitably and rather
what we see happening is concentrating wealth and power
provided to a selected group of people, corporations and nations,
and marginalizing others, that is, if global opportunities are not
shared better, then the failures in the last decades in growth of
nations will continue. UNESCO [17], outlined significant changes
that are needed to occur in pre-service teacher education
programs as guidelines for future implementation, this is
because there is the need to select and prepare a new generation
of teachers to be equipped with the skills, knowledge and values
to help their cultural differences and social disadvantages.
The Western World political observers and leaders already
judged African countries to be practicing democracy only in
the beginning of the 1990s, and they have already concluded
that unless African countries accept western ideas of practicing
democracy, especially, formulated with conditionalities of donor
countries including financial institutions, the future of Africa
development is bound to be bleak [18]. It has been noted that
the over reliance of African countries continuously on foreign
aid only increased bilateral and multilateral aid agencies to
influence their opportunities in policy making towards the
African continent and these have been linked to donor supports
being giving to African governments. For example, prescriptions
for changes in both political and economic policies designed by
African governments’ such as education and research. Also, the
new world created has interest and influence of the Western
countries gained considerably greater advantage over African
governments [19].
According to Doe (2005), he stated that Ghana has not been
advanced in technology, systems, or policy-making approach in
the past years. Since independence, Ghana only has a mimicked
or funny kind of public service administration and management
practices through coercion/force/pressure from the developed
countries and the International Development Agencies. Under
the path coefficient IDA to PubAmin as a moderator variable has
stronger relationship than, as a moderator in executing or having
a less final impact and effect towards Edu_Res. This explains the
fact that International Development Agencies or organizations
deals with the African governments than just directly donating
or supporting in the Area of Education and Research needs of the
country. There has been discriminant validity towards Education
and Research. There is also reliability at Education and Research,
and Public Administration as an adequate model whereas
International Development Agencies has very weak composite
towards Education and Research in general. According to the
p-value at p>0.05 shows that IDA to Edu_Res is insignificant as
in H1: IDA support for Edu_Res is not IDA major policy [20,21].
H2: IDA to PubAdmin (government) is significant because
it confirms that IDA only has a policy of given support to the
PubAdmin (government) and not probably support any other
developmental project. H3: PubAdmin (government) to Edu_Res
has weak evidence because PubAdmin in turn does not really
use the supports it receives by IDA’s to build or sponsor good
Education and Research. H2: is even evident that the confidence
level of these research findings is at IDA to PubAdmin. Therefore,
based on the above conclusions, it is important for both the
African governments and the international development
agencies or organizations such as the IMF, World Bank, EU etc
to move away from close door kind of policies and be more
proactive in tackling educational needs as well as research
development to enhance true development across sections of
African economies. Hence, there must be proper transparency
and accountability so that the people will feel the impact of IDA
presents and their supports. In this case there may be the need
for future study into the IDA policies implementation on African
governments to include large population of probability sampling
to contradict or confirm same. Projects that are lacking in the educational research area, within the curriculum of educational
activities must be given proper attention by IDA and the Public
Admin or the Central Governments. This will be the only best way
to develop human capital for Africans and thereby improving
on the governments’ Human Resource Management policies as
established.
For More Articles in Annals of Social Sciences & Management studies
Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/asm/index.php
For More Open Access Journals In Juniper Publishers Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php


Comments
Post a Comment